-
Xinqi Development Zone, Leliu, Foshan, Guangdong

5 Cost-Quality Facts: Acrylic vs PC Diffusers
Table of Contents
Introduction
In the design of LED lighting systems, the material selection of light diffusers directly affects the lighting effect and product life. According to the Grand View Research report, the global light diffusion material market is expected to reach US$5.78 billion in 2028, of which acrylic and polycarbonate account for 68% of the market share. This article compares 10 key performance indicators to help you make a wise choice.
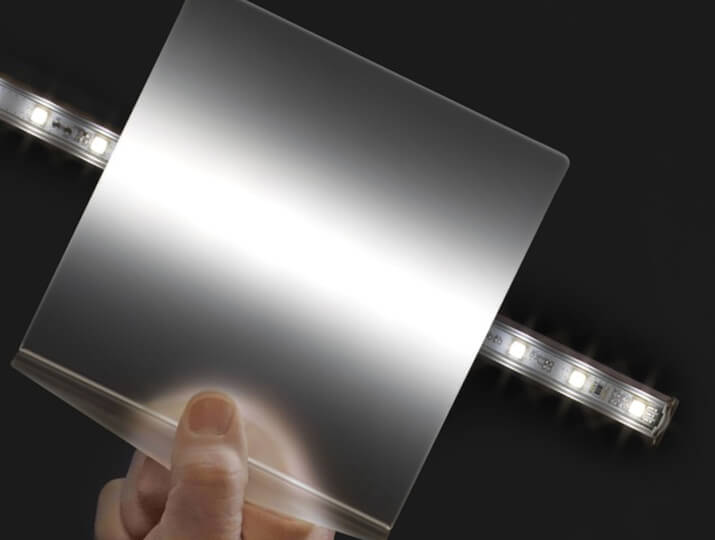
1. Basic performance comparison
Light transmission efficiency
Acrylic diffusers lead with a light transmittance of 92% (PlasticsToday data), and its special microsphere structure can evenly scatter light and reduce brightness loss. The light transmittance of polycarbonate is about 88-90%, and more diffusers need to be added to achieve similar effects.
Impact strength
Polycarbonate shows an absolute advantage, and its impact resistance is 250 times that of acrylic. In high-risk scenarios such as stadiums, polycarbonate can withstand 200J/cm² impact energy, while acrylic can only withstand 0.8J/cm².
2. Environmental adaptability
Weather resistance
Polycarbonate remains stable in the range of -40℃~120℃ (Omnexus research), which is suitable for polar scientific research equipment. Acrylic will soften and deform above 85℃, but has better UV stability. A 5-year outdoor test in Florida showed that the yellowing index was only ΔE<2.
Fire rating
Both are UL94 certified, but perform differently:
Acrylic: V2 level, continues to burn for <30 seconds after leaving the fire
Polycarbonate: V0 level, self-extinguishing within 10 seconds (UL laboratory report)

3. Processing and economy
Molding complexity
Acrylic can be cold-bent at room temperature, with a minimum bending radius of 3 times the thickness of the sheet. Polycarbonate needs to be heated to 160°C for molding, but supports more complex hyperbolic designs, such as the 0.5mm precision structure required for automotive HUD displays.
Cost-effectiveness
The price of acrylic raw materials is 35-40% lower than that of polycarbonate (ICIS 2023 price index). Calculated based on a 1.2m×2.4m standard plate:
Polycarbonate: $280-350
4. Surface properties
Wear resistance index
The surface hardness of acrylic reaches Rockwell M90, and it is not easy to leave marks in daily friction. Polycarbonate is only M70, and a hardening coating needs to be added, but the haze can be improved through surface texture design.
Chemical resistance
Polycarbonate has better resistance to acid and alkali solutions:
Resistance to 10% sulfuric acid solution: >500 hours
Resistance to 5% sodium hydroxide: >300 hours (Data source: ChemicalResistanceGuide.com)
5. Sustainable development
Environmental protection characteristics
Acrylic recycling rate reaches 92%, and processing energy consumption is 28% lower than polycarbonate (Ellen MacArthur Foundation report). However, the closed-loop recycling system of polycarbonate in the automotive field is more mature, and the BMW i series has achieved 100% recycling.
Service life
Accelerated aging test shows:
—Acrylic: 25-year light transmittance retention rate in indoor environment >85%
—Polycarbonate: 15-year impact resistance reduction in outdoor use <10%
Application scenario decision matrix
| Indicator | Commercial lighting | Industrial lighting | Outdoor lighting | Decorative lighting |
| Light transmittance requirements | Acrylic | Acrylic | Polycarbonate | Acrylic |
| mpact resistance requirements | Polycarbonate | Polycarbonate | Polycarbonate | Acrylic |
| Budget constraints | Acrylic | Acrylic | Polycarbonate | Acrylic |
FAQs
1. FAQ: Acrylic vs Polycarbonate Light Diffusers
Acrylic diffusers provide 92% light transmission vs polycarbonate’s 88-90%
2. How long do they last outdoors?
Acrylic maintains >85% light transmission for 25+ years indoors vs polycarbonate’s 15-year outdoor durability (MaterialTestingLab).
3. Which material resists chemicals better?
Polycarbonate withstands 10% sulfuric acid for 500+ hours (ChemicalResistanceGuide).
4. Which handles extreme temperatures better?
Polycarbonate operates in -40°C~120°C, while acrylic softens above 85°C (Omnexus).
Conclusion
Acrylic diffusers are still the preferred solution for commercial lighting due to their 92% light transmittance and cost advantages. However, when encountering extreme temperatures, mechanical shock or chemical corrosion environments, the excellent performance of polycarbonate is irreplaceable. It is recommended that manufacturers establish a graded material selection system based on application scenarios, such as:
Basic type: acrylic (meets 85% of conventional needs)
Enhanced type: polycarbonate (special environment application)
For customized material selection solutions, please refer to the International Illumination Commission technical report or consult a material engineer. The latest nano-composite technology has developed PC/PMMA co-extruded sheets, combining the advantages of both, which will be the development direction of the next generation of light diffusers.